


Next: Dependent
Up: Module 8: Introduction to
Previous: Contents
Contents
1.1. The t distribution
One Sample t test
- An extension of the Z-test with a sample mean.
- Still comparing a sample mean to a population mean.
- But, we have the problem of an unknown
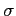 and
and 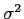 .
.
- Both
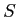 and
and 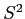 are biased because samples are by their very nature, smaller than the population(s) they represent.
are biased because samples are by their very nature, smaller than the population(s) they represent.
- So, we apply a progressive correction (
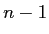 ), to arrive at an unbiased estimate of the population variance.
), to arrive at an unbiased estimate of the population variance.
- We say progressive correction because; as sample size (
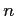 ) gets larger, the correction has less effect.
) gets larger, the correction has less effect.
- Larger sample
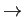 includes more of the population
includes more of the population 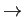 less bias.
less bias.
- Therefore, less correction is needed as sample size increases.
Degrees of Freedom (df)
We call this progressive correction the degrees of Freedom (df).
- The number of scores in a sample which are ``free to vary''.
- If you know the mean and all but one of the scores, you can figure the score you don't know.
- So, for one sample t test:
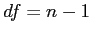
- Now we can go on with some of the `usual stuff'.
Comparison Distribution Changes
- Because we are estimating the population variance, we use the t distribution (instead of the Z distribution as was done previously).
- The t distribution is not normally distributed, due to more error in estimation (i.e., estimating the unknown
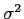 ).
).
- Different table, similar procedure for finding the cutoff sample score associated with
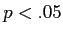 , or any other significance level.
, or any other significance level.
- But, you must take into account sample size; meaning, the df in order to find
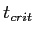
An Excerpt from the t distribution table
Table 1: t Critical Values
|
1-tailed |
df |
.10 |
.05 |
.025 |
.01 |
|---|
|
2-tailed |
df |
.20 |
.10 |
.05 |
.02 |
|
|
1 |
3.078 |
6.314 |
12.710 |
31.821 |
|
|
2 |
1.886 |
2.920 |
4.303 |
6.965 |
|
|
3 |
1.638 |
2.353 |
3.182 |
4.541 |
|
|
4 |
1.533 |
2.132 |
2.776 |
3.747 |
|
|
5 |
1.476 |
2.015 |
2.571 |
3.365 |
|
|
6 |
1.440 |
1.943 |
2.447 |
3.143 |
|
|
etc. |
|
|
|
|
Degrees of freedom in the left column and significance level along the top rows.
Calculating the One Sample t
- Also referred to as
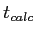 which is compared to
which is compared to 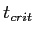
- Recall,
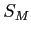 is the standard deviation of a distribution of means.
is the standard deviation of a distribution of means.
- First, calculate
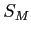 (
(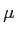 is given):
is given):
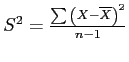 then
then
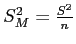 then
then
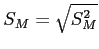
- Which leads to:
- The formula below is the one used here but, all three above are equivalent (
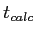 ).
).
1.2. One Sample t-test Example
NHST Example
Research question:
- Does this class of four students get less sleep than all UNT students (
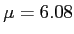 hours)?
hours)?
- Step 1: Define the populations and restate the research question as null and alternative hypotheses.
- Population 1: Students in this class.
- Population 2: All other UNT students.
- Note, the Alternative hypothesis (
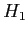 ) is directional: one-tailed test.
) is directional: one-tailed test.
Step 2: Comparison Distribution
Table 2: Comparison dist. (estimate 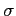 with
with 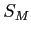 )
)
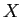 |
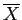 |
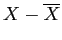 |
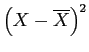 |
|
5 |
4 |
1 |
1 |
|
3 |
4 |
-1 |
1 |
|
6 |
4 |
2 |
4 |
|
2 |
4 |
-2 |
4 |
|
16 |
|
|
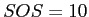 |
Step 3: Determine the critical score
- Determine the cutoff sample score.
- Significance level = .05, one-tailed test,
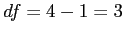
- Look in the appropriate column of the t table.
- One-tailed, significance level = .05
- Critical t value is 2.353
- Which means, we need
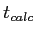 to be greater than
to be greater than |2.353| (absolute value of 2.353) to find a significant difference.
Step 4: Calculate t (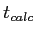 )
)
- From previous calculating, we have:
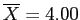
,
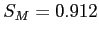
- So, we can plug in the values, including the population mean which was given.
Step 5: Compare and Make a Decision
- Since
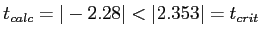 we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
- The interpretation is...Students in this class (
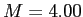 ) do not sleep significantly fewer hours than all other students at UNT (
) do not sleep significantly fewer hours than all other students at UNT (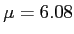 ),
),
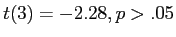 .
.
- Do not be tempted to say something like; nearly significant, just missed significance, etc.
- Although the sample mean is numerically smaller, it is not statistically significantly smaller.
- Remember, we have a very small sample size, so we would need a very large mean difference to achieve significance (or a larger sample).
1.3. Effect Size
Effect Size
- The appropriate effect size measure for the one sample t test is Cohen's d.
- Calculation of d in its general form (as it was with the Z-test) is:
- However, we do not know the population standard deviation (
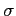 ) in the t situation, so we estimate with
) in the t situation, so we estimate with
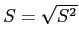
- So, although we have a large effect size (standardized difference), we did not achieve statistical significance. However, keep in mind that with a larger sample, this amount of mean difference may have been significant.
- Statistical significance is directly tied to sample size, effect size is not.
1.4. Using Delta for Statistical Power
Statistical Power and Sample Size
- Calculating power with the one sample t test is slightly different than with the Z-test.
- Here, we introduce something called the Non-Centrality Parameter (NCP).
- The NCP takes its name from the fact that if
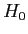 is false, the distribution of our statistic will not be centered on zero, but on something called delta.
is false, the distribution of our statistic will not be centered on zero, but on something called delta.
- Thus, the distribution is non-central.
- The symbol for delta is:
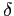
- In the context of the one sample t test, delta is calculated as follows:
Statistical Power and Sample Size
- To calculate delta (
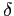 ) for our current example:
) for our current example:
- With the significance level (.05, one-tailed), we can look up power in a
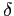 table.
table.
which is not terribly meaningful once the study has been completed.
- However, we can now use
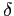 to calculate sample size a-priori for a given power (prior to collecting data for the next study).
to calculate sample size a-priori for a given power (prior to collecting data for the next study).
- Where
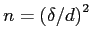
- This type of power calculation (figuring a-priori sample size) is very useful.
1.5. 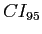
Calculating a Confidence Interval
- Confidence intervals allow us to go beyond NHST and offer us an idea of the location of a population mean (
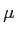 ).
).
- We need three numbers to calculate a confidence interval:
- The Standard Error (SE) which is also known as the standard deviation of a distribution of means:
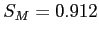
- The critical value from our current study:
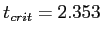
- And the mean of our sample:
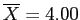
- Recall the general formulas for a confidence interval from Module 6:
Calculating a CI
- In this example, we are calculating a 95% confidence interval (
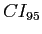 ) because our critical value was based on a significance level of .05 (1 - .05 = .95 or 95%).
) because our critical value was based on a significance level of .05 (1 - .05 = .95 or 95%).
-
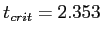 ,
, 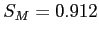 ,
,
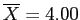
- If we were to take an infinite number of samples of students in this class, 95% of those samples' means would be between 6.146 and 1.854 hours of sleep.
- Remember, the population mean is fixed (but unknown); while each sample has its own mean (sample means fluctuate).
 Considerations and Interpretations
Considerations and Interpretations
The current example resulted in
 .
.
- Notice the population 2 mean (
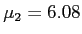 ), representing all UNT students, falls inside our interval.
), representing all UNT students, falls inside our interval.
- Recall, we did not reject the null; meaning our sample did come from population 2, not a distinct population (i.e. population 1).
- If
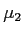 were greater than 6.146, then we would have rejected the null hypothesis and inferred that our sample came from population 1; meaning, population 1 would have been significantly different from population 2.
were greater than 6.146, then we would have rejected the null hypothesis and inferred that our sample came from population 1; meaning, population 1 would have been significantly different from population 2.
- Important: the interval is not interpreted as ``we are 95% confident that population 1's mean is between 6.146 and 1.854.''
- We are dealing with a sample; we do not know what
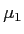 is; so, we can not know what that interval would be.
is; so, we can not know what that interval would be.
1.6. Summary of Section 1
One Sample t test Usage?
Unfortunately...
- The one sample t test is essentially never used, but it servers a good purpose to familiarize us with the t distribution.
- Occasionally, we know both
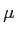 and
and 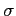 , for instance with SAT or GRE scores, which necessitates the Z-test.
, for instance with SAT or GRE scores, which necessitates the Z-test.
- Generally, we do not know
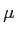 or
or 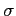 so the one sample t test is not frequently used.
so the one sample t test is not frequently used.
- Instead, as we will see; we estimate population values with sample statistics and compare samples to infer effects in the general population(s) of interest.
- The t distribution is used for other types of t tests which will be covered shortly.
Summary of Section 1: One Sample t Test
Section 1 covered the following topics:
- Introduced the t distribution
- One Sample t test
- Cohen's d Effect Size
- Use of delta (
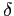 ) for Statistical Power
) for Statistical Power
- Use of delta (
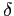 ) for calculating a-priori sample size
) for calculating a-priori sample size
- Calculation of Confidence Intervals.



Next: Dependent
Up: Module 8: Introduction to
Previous: Contents
Contents
jds0282
2010-10-15
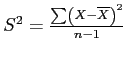
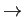 includes more of the population
includes more of the population 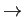 less bias.
less bias.
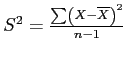
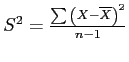 then
then
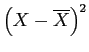
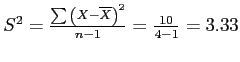
![]() )
)
![]() Considerations and Interpretations
Considerations and Interpretations
![]() .
.