|
Use
the Merge function to add cases
Task: Use the
Merge function to add cases from 'ExampleData002' to ‘ExampleData001'.
Start off by importing the
ExampleData001.sav
into the Data Editor window of PASW / SPSS (from this point forward
referred to as simply SPSS). You will also need
ExampleData002.sav;
so download and save it to your desktop or some other location (but
do not open it; only open ExampleData001).
First, go to Data, Merge Files, Add Cases...
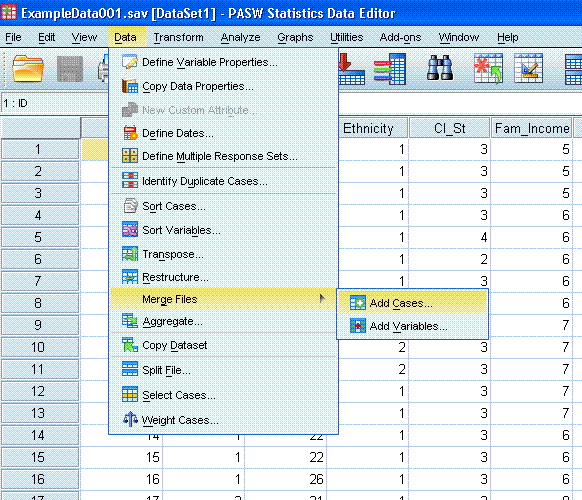
Now, you should see the following dialog box.
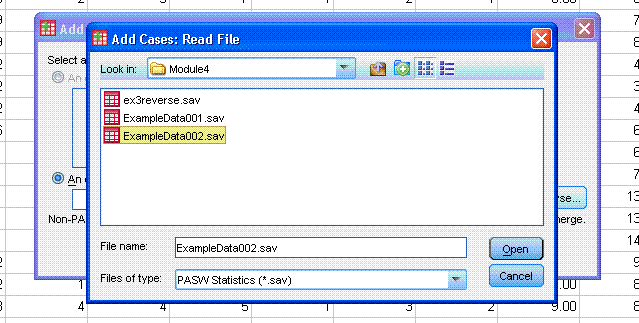
Click on the "Browse..." button and find 'ExampleData002.sav' from
where you downloaded and saved it earlier.
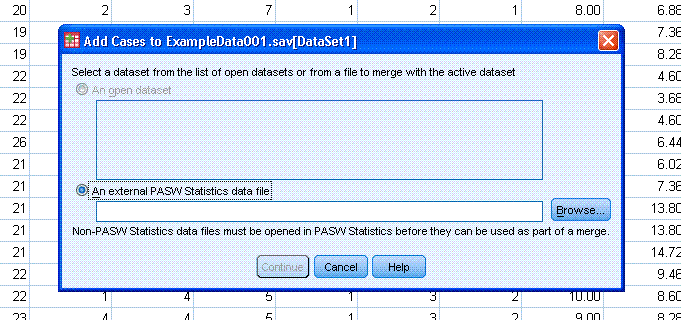
Then click on the "Open" button.
You should now have it listed as the file you want
to merge with the (already open) ExampleData001.sav.
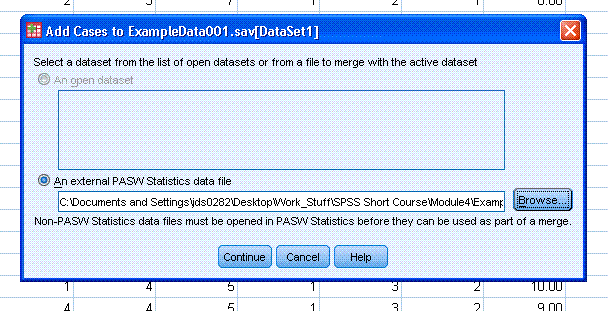
Now click the "Continue" button and you should
then see the Add Cases dialog (shown below). Now click the "OK" button
to complete the merge function. However, you may want to continue
reading below.
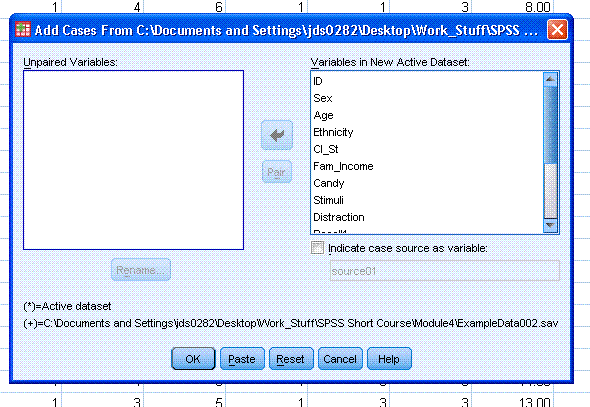
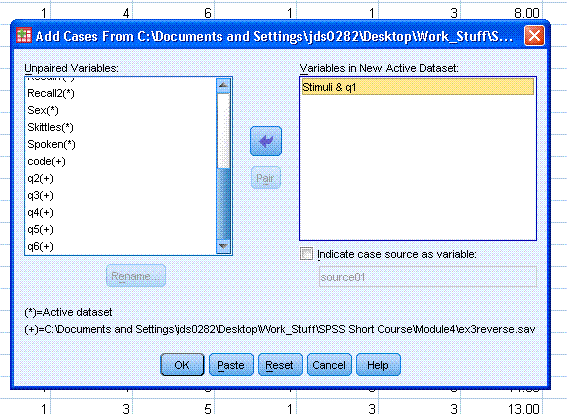
There are a few things to discuss about this
dialog. First, the current example is very clean and no "Unpaired
Variables:" are present. If there were variables in either data set
which were not present in the other data set, they would be listed in
the "Unpaired Variables:" box to the left. Second, those unpaired
variables would be identified by the legend just below that box. Each
variable would be listed by its name, but would also have a symbol
associated with it which would identify the data set it came from. The
symbols, as seen in the legend, are an * for the active data set and a
+ for the incoming data set. The active data set is the one you opened
first; while the incoming data set is the one you had to browse to find
in the previous steps. As an example; look at the images below in which
the active data set is ExampleData001 and the incoming data set is
ex3reverse.sav. Both data sets have unique variables and do not share
any variables in common.
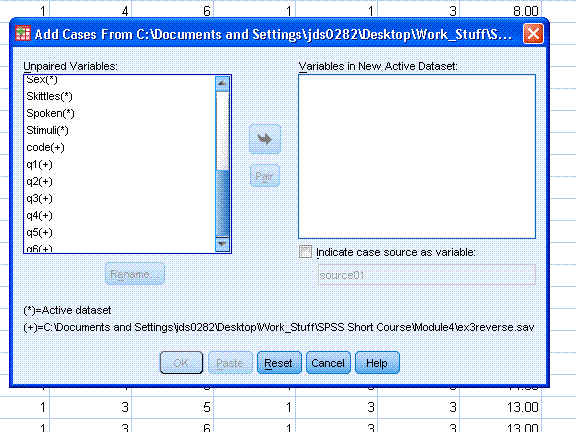 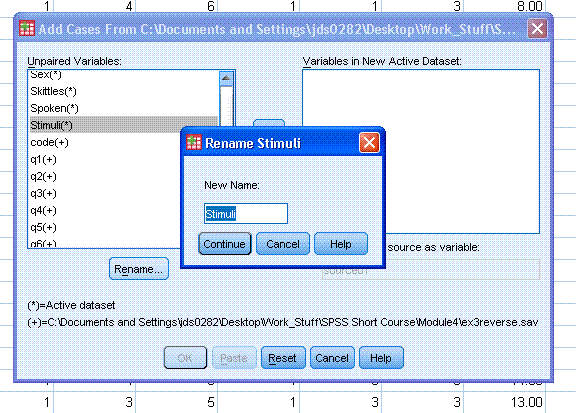
These types of mis-matches can occur due to data
sets having different names for the same variable. A frequent example
of this is gender/sex. When this occurs, a variable is present in both
data sets, but carries a different name in each; you can use the
"Rename..." button to rename one of them so they match.
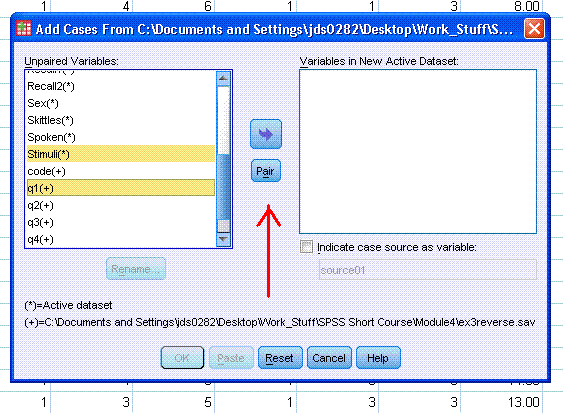
You can also use the 'Pair' button after selecting
two variables at one time to combine differing names.
|


